Discrete Laplacians for General Polygonal and Polyhedral Meshes

Astrid Bunge
TU Dortmund

Marc Alexa
TU Berlin

Mario Botsch
TU Dortmund
Slides are available online
Problem Setting
Solve PDEs on surface meshes and volume meshes
 Surface mesh
Surface mesh  Volume mesh
Volume mesh
Laplacian is a central operator
- Gradient (direction of steepest ascent) \[ \grad f(u,v) \;=\; \vector{ \pdiff{f}{u} \\ \pdiff{f}{v} } \]
- Divergence (magnitude of source or sink) \[ \func{div}\of{\vec{f}(u,v)} \;=\; \func{div} \vector{f_1(u,v) \\ f_2(u,v)} \;=\; \pdiff{f_1}{u} + \pdiff{f_2}{v} \]
- Laplace (difference to average of local neighborhood) \[ \laplace f(u,v) \;=\; \func{div} \grad f \;=\; \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial u^2} + \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial v^2} \]
Diffusion Equation: \(\dot f = \lambda \laplace f\)
Laplace Equation: \(-\laplace f = 0\)
Discrete Laplacian has various applications
- Mean Curvature
- Smoothing & Fairing
- Parameterization
- Deformation
- Geodesics Distances
- …
Discrete Laplacians for Polygonal/Polyhedral Meshes
 Surface Meshes:
Surface Meshes: Triangles Polygons  Volume Meshes:
Volume Meshes: Tetrahedra Polyhedra
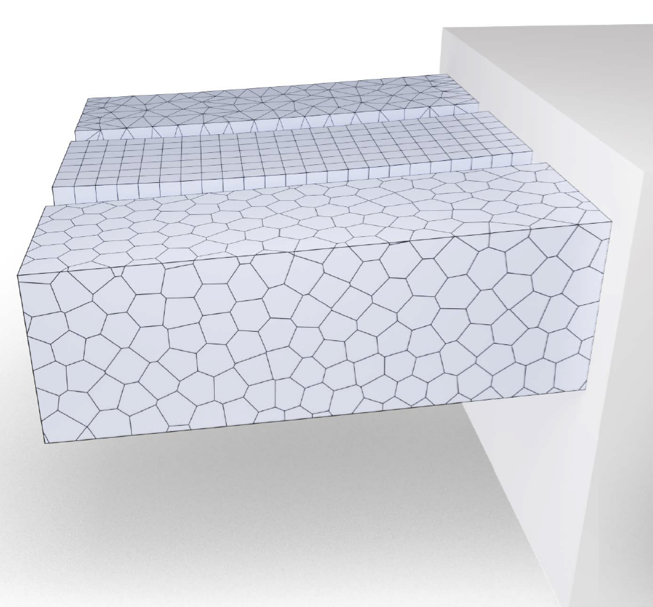
Artist-Made Polygon Meshes
Adaptive Refinement
Cutting & Fracturing
Discrete Laplacians for Polygonal Meshes
 Surface Meshes:
Surface Meshes: Triangles Polygons  Volume Meshes:
Volume Meshes: Tetrahedra Polyhedra
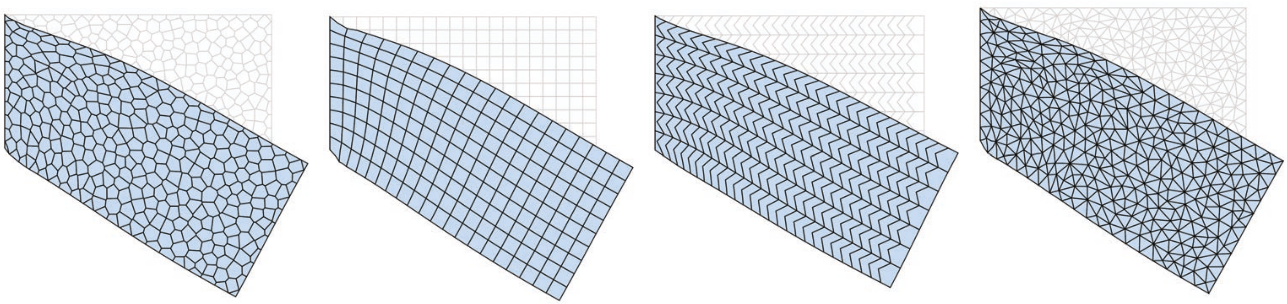
Triangulate the Polygons?
Outline
- Introduction
- Laplacian for Triangle Meshes
- Laplacian for Polygon Meshes
- Martin et al., Polyhedral finite elements using harmonic basis functions, SGP 2008
- Alexa & Wardetzky, Discrete Laplacians on general polygonal meshes, SIG 2011
- de Goes et al., Discrete differential operators on polygonal meshes, SIG 2020
- Bunge et al., Polygon Laplacian made simple, EG 2020
- Bunge et al., The Diamond Laplace for polygonal and polyhedral meshes, SGP 2021
- Bunge et al., Variational quadratic shape functions for polygons and polyhedra, SIG 2022
- Comparisons & Conclusion
Triangle Meshes
- Connectivity / Topology
- Vertices \(\mathcal{V} = \{ v_1, \dots, v_n \}\)
- Edges \(\mathcal{E} = \{ e_1, \dots, e_k \}\), \(e_i \in \mathcal{V} \times \mathcal{V}\)
- Faces \(\mathcal{F} = \{ f_1, \dots, f_m \}\), \(f_i \in \mathcal{V} \times \mathcal{V} \times \mathcal{V}\)
- Geometry
- Vertex positions \(\{ \vec{x}_1, \dots, \vec{x}_n \}\), \(\vec{x}_i \in \R^3\)
Functions on Triangle Meshes
- Define a piecewise linear function on a triangle mesh as \[f(\vec{x}) = \sum_{i \in \set{V}} f_i \varphi_i(\vec{x})\]
- Assign function values \(f_i\) to vertices \(v_i\) with positions \(\vec{x}_i\)
- Assign linear “hat” basis functions \(\varphi_i(\vec{x})\) to vertices \(v_i\)
- Equivalent to barycentric interpolation of \(f_i\) within triangles
Barycentric Coordinates as Shape Functions
- Piecewise linear functions
- Interpolate nodal data: \(\varphi_i\of{\vec{x}_j} = \delta_{ij}\)
- Partition of unity: \(\sum_i \varphi_i\of{\vec{x}} = 1\)
- Barycentric property: \(\sum_i \varphi_i\of{\vec{x}} \vec{x}_i = \vec{x}\)
- \(C^0\) across elements, \(C^1\) within elements
Laplace Matrix & Mass Matrix
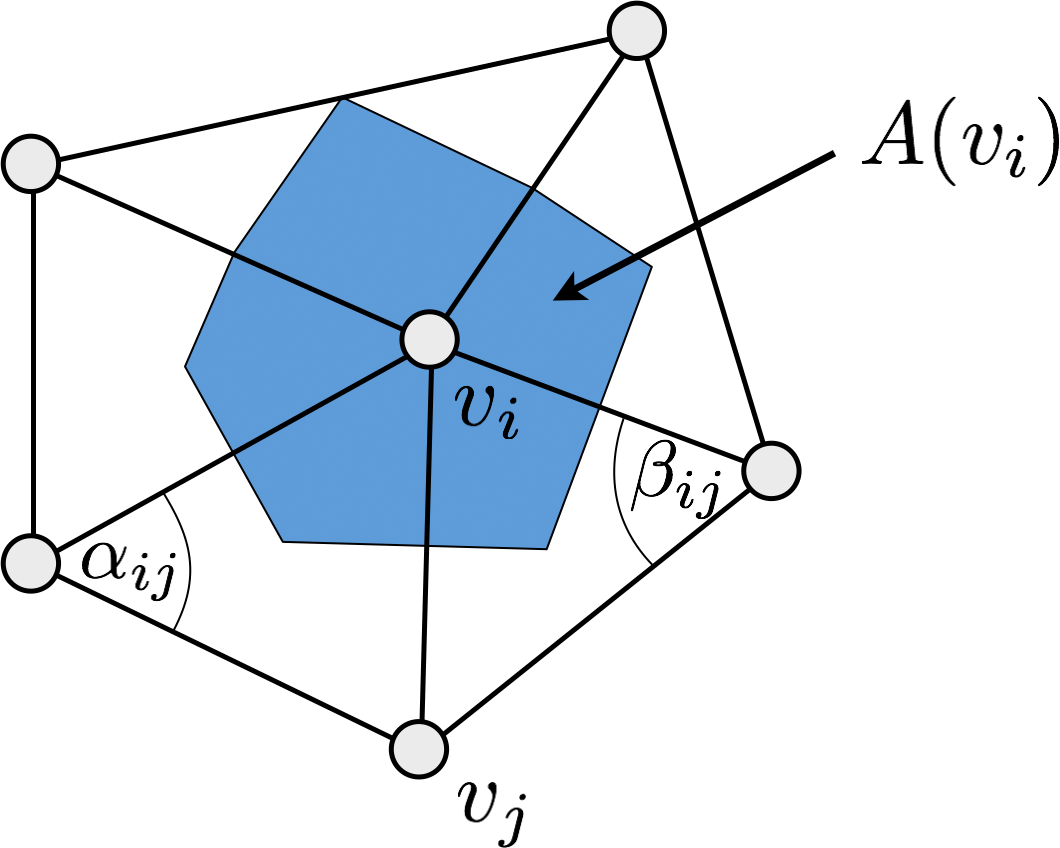
\[ \small \begin{eqnarray*} \mat{L}_{ij} &=& -\int \grad \varphi_i \cdot \grad \varphi_j &=& \begin{cases} \frac{\cot\alpha_{ij}+\cot\beta_{ij}}{2} & \text{if } j\in\set{N}\of{i} \,, \\[0.5em] \displaystyle -\sum_{k\in\set{N}\of{i}} \mat{L}_{ik} & \text{if } j=i \,, \\[0.3em] 0 & \text{otherwise}. \end{cases} \\[1em] \mat{M}_{ij} &=& \int \varphi_i \, \varphi_j &=& \begin{cases} \frac{\abs{t_{ijk}} + \abs{t_{jih}}}{12} & \text{if } j\in\set{N}\of{i}\,, \\[0.5em] \displaystyle \sum_{k\in\set{N}\of{i}} \mat{M}_{ik} & \text{if }j=i \,,\\[0.3em] 0 & \text{otherwise}. \end{cases} \end{eqnarray*} \]
Local to Global Assembly
Properties
- Symmetry
- Continuous Laplacian is selfadjoint
- Locality
- Laplacian of a function \(u\) at point \(\vec{x}\) should only depend on small neighborhood
- Linear precision
- Laplacian of linear functions should be zero on planar regions
- Negative semi-definiteness
- Ensures that Dirichlet energy does not switch signs
- Null property
- Kernel of the Laplacian should only contain constant functions
- Positive weights
- Sufficient condition for maximum principle
Quiz
Which property does the cotangent Laplacian not satisfy?
- Symmetry
- Locality
- Linear precision
- Negative semi-definiteness
- Null property
- Positive weights
Properties
- Symmetry
- Locality
- Linear precision
- Negative semi-definiteness
- Null property
- Positive weights
Poisson System on 2D Triangle Meshes
Poisson System on 2D Triangle Meshes
7.28224, 14.5124, 28.9698, 57.8831, 115.709
Cotan Laplacian, 0.0184139, 0.00457148, 0.00115444, 0.000291485, 7.33316E-05
<!--
{
"options": {
"scales": {
"x": {
"title": {
"text": "inverse mean edge length",
"display": true
}
},
"y": {
"title": {
"text": "L2 error",
"display": true
}
}
}
}
}
-->Poisson System on 2D Triangle Meshes
7.28224, 14.5124, 28.9698, 57.8831, 115.709
Cotan Laplacian, 0.0184139, 0.00457148, 0.00115444, 0.000291485, 7.33316E-05
<!--
{
"options": {
"scales": {
"x": {
"title": {
"text": "inverse mean edge length",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
},
"y": {
"title": {
"text": "L2 error",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
}
}
}
}
-->Outline
- Introduction
- Laplacian for Triangle Meshes
- Laplacian for Polygon Meshes
- Martin et al., Polyhedral finite elements using harmonic basis functions, SGP 2008
- Alexa & Wardetzky, Discrete Laplacians on general polygonal meshes, SIG 2011
- de Goes et al., Discrete differential operators on polygonal meshes, SIG 2020
- Bunge et al., Polygon Laplacian made simple, EG 2020
- Bunge et al., The Diamond Laplace for polygonal and polyhedral meshes, SGP 2021
- Bunge et al., Variational quadratic shape functions for polygons and polyhedra, SIG 2022
- Comparisons & Conclusion
Barycentric Coordinates
- Piecewise linear functions
- Interpolate nodal data: \(\varphi_i\of{\vec{x}_j} = \delta_{ij}\)
- Partition of unity: \(\sum_i \varphi_i\of{\vec{x}} = 1\)
- Barycentric property: \(\sum_i \varphi_i\of{\vec{x}} \vec{x}_i = \vec{x}\)
- \(C^0\) across elements, \(C^1\) within elements
Generalized Barycentric Coordinates
Piecewise linear functions- Interpolate nodal data: \(\varphi_i\of{\vec{x}_j} = \delta_{ij}\)
- Partition of unity: \(\sum_i \varphi_i\of{\vec{x}} = 1\)
- Barycentric property: \(\sum_i \varphi_i\of{\vec{x}} \vec{x}_i = \vec{x}\)
- \(C^0\) across elements, \(C^1\) within elements
Generalized Barycentric Coordinates
- Wachspress Coordinates
- Wachspress, Warren
- Mean Value Coordinates
- Floater, Hormann, Ju, Wicke
- Maximum Entropy Coordinates
- Sukumar, Hormann
- Harmonic Coordinates
- Joshi, Martin
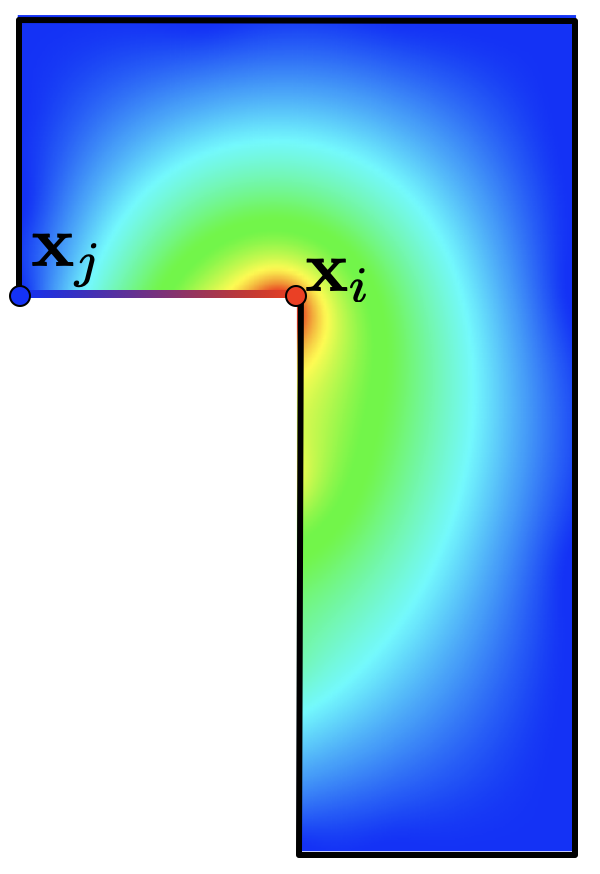
Harmonic Coordinates
- Definition
- Interpolate nodal data: \(\varphi_i(\vec{x}_j) = \delta_{ij}\)
- Linear (=harmonic) on edges
- Harmonic in interior: \(\laplace\varphi_i = 0\)
- Computation
- Method of fundamental solutions
- Approximate shape functions \(\varphi_i\) by RBFs \(\psi_k\) \[\varphi_i(\vec{x}) = \sum_k w_k \, \psi_k\of{\vec{x}} + \pi_1\of{\vec{x}}\]
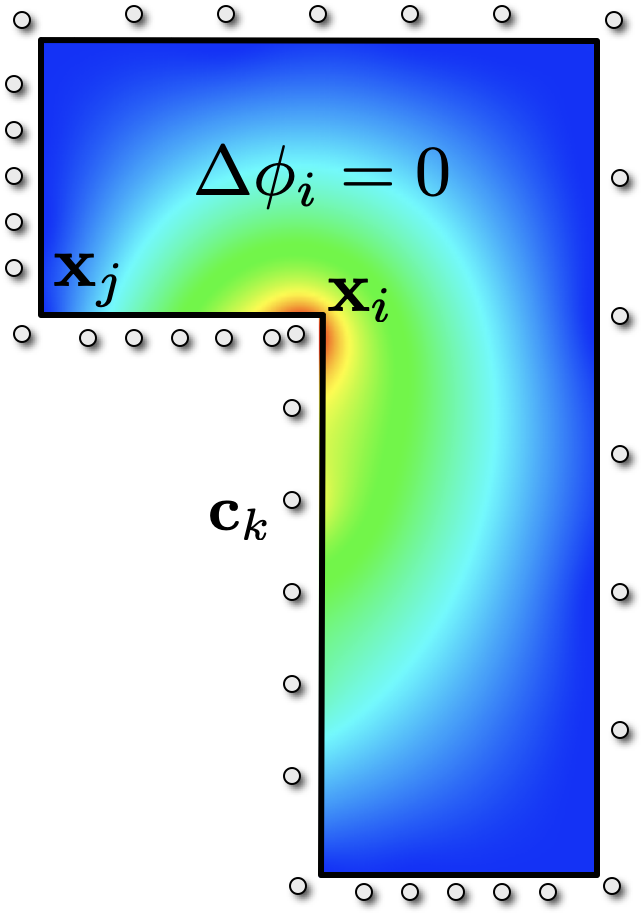
Quiz
For which property is the polynomial term \(\pi_1\of{\vec{x}}\) crucial? \[\varphi_i(\vec{x}) = \sum_k w_k \, \psi_k\of{\vec{x}} + \pi_1\of{\vec{x}}\]
- Symmetry
- Locality
- Linear precision
- Negative semi-definiteness
- Null property
- Positive weights
Laplace Matrix & Mass Matrix
\[ \small \begin{eqnarray*} \mat{L}_{ij} &=& -\int \grad \varphi_i \cdot \grad \varphi_j &=& \color{red}{\xcancel{ \begin{cases} \frac{\cot\alpha_{ij}+\cot\beta_{ij}}{2} & \text{if } j\in\set{N}\of{i} \,, \\[0.5em] \displaystyle -\sum_{k\in\set{N}\of{i}} \mat{L}_{ik} & \text{if } j=i \,, \\[0.3em] 0 & \text{otherwise}. \end{cases} }} \\[1em] \mat{M}_{ij} &=& \int \varphi_i \, \varphi_j &=& \color{red}{\xcancel{ \begin{cases} \frac{\abs{t_{ijk}} + \abs{t_{jih}}}{12} & \text{if } j\in\set{N}\of{i}\,, \\[0.5em] \displaystyle \sum_{k\in\set{N}\of{i}} \mat{M}_{ik} & \text{if }j=i \,,\\[0.3em] 0 & \text{otherwise}. \end{cases} }} \end{eqnarray*} \]
On triangles, harmonic coordinates reproduce barycentric coordinates
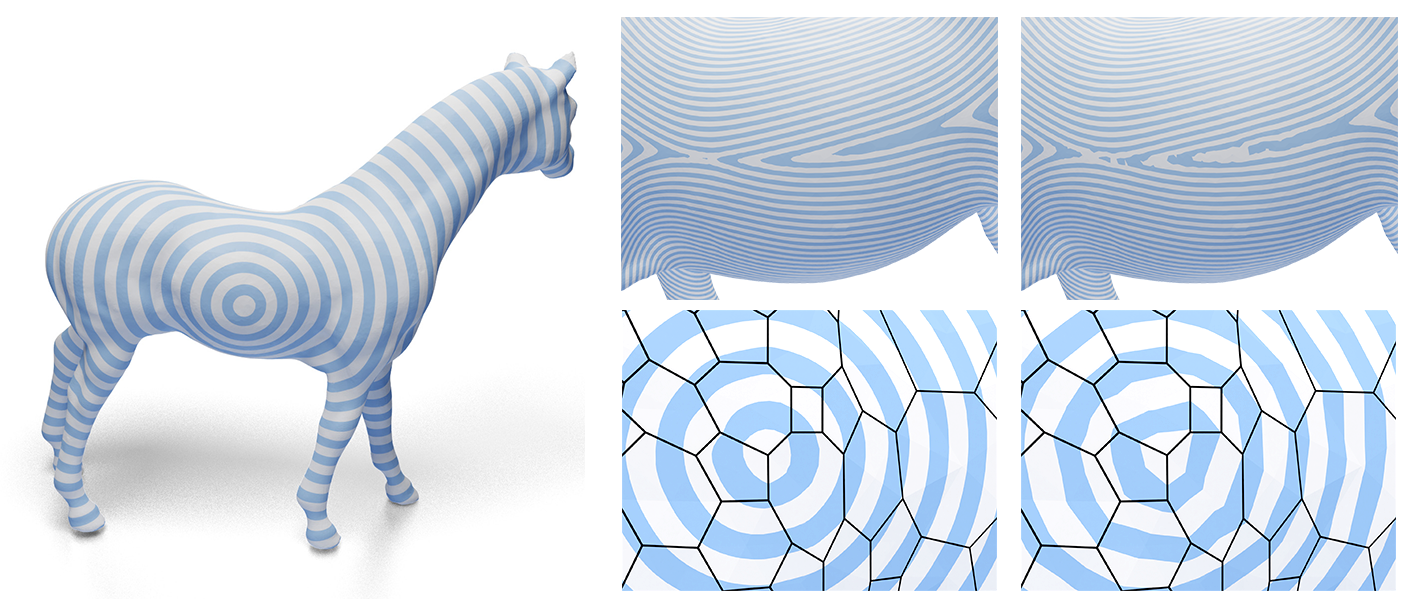
Demo: Parameterization
Properties
- Symmetry
- Locality
- Linear precision
- Negative semi-definiteness
- Null property
- Positive weights
Poisson System on 2D Voronoi Meshes
Poisson System on 2D Voronoi Meshes
13.5053, 28.5194, 58.8386, 119.78, 241.153
Harmonic, 0.00951959, 0.00236579, 0.000699382, 0.000188646, 5.46139E-05
<!--
{
"options": {
"scales": {
"x": {
"title": {
"text": "inverse mean edge length",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
},
"y": {
"title": {
"text": "L2 error",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
}
}
}
}
-->Expected convergence rate 😄 Expensive to compute, evaluate, and integrate 😢
Harmonic Coordinates on Polyhedral Meshes
- Approximate 3D shape functions \(\varphi_i\) with RBFs \(\psi_k\), just as before \[\varphi_i(\vec{x}) = \sum_k w_k \, \psi_k\of{\vec{x}} + \pi_1\of{\vec{x}}\]
- Changes:
- Approximate 2D shape functions for each of the polyhedron’s faces
- Sample harmonic Dirichlet boundary conditions with 2D basis
- Change RBFs \(\psi_k\) to fundamental solution of 3D Laplace equation
Harmonic Finite Elements
Outline
- Introduction
- Laplacian for Triangle Meshes
- Laplacian for Polygon Meshes
- Martin et al., Polyhedral finite elements using harmonic basis functions, SGP 2008
- Alexa & Wardetzky, Discrete Laplacians on general polygonal meshes, SIG 2011
- de Goes et al., Discrete differential operators on polygonal meshes, SIG 2020
- Bunge et al., Polygon Laplacian made simple, EG 2020
- Bunge et al., The Diamond Laplace for polygonal and polyhedral meshes, SGP 2021
- Bunge et al., Variational quadratic shape functions for polygons and polyhedra, SIG 2022
- Comparisons & Conclusion
DEC Polygon Laplacians
- Generalize DEC to non-planar polygons
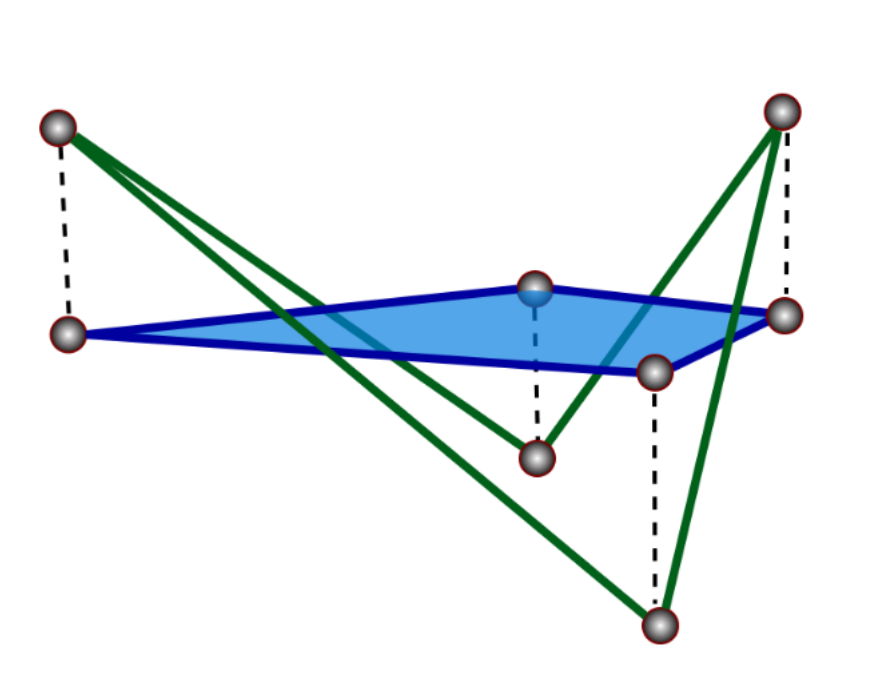
- Discretization of \(\laplace f = \delta d f\) (Laplace-de Rham)
- The exterior derivative \(d\) becomes the difference operator \(\mat{d}\)
- The co-differential \(\delta\) can be discretized as \(\mat{M}_0^{-1} \mat{d}\T \mat{M}_1\)
- Putting it together: \(\laplace \vec{u} \;\approx\; -\mat{M}_0^{-1} \mat{d}\T \mat{M}_1 \mat{d}\, \vec{u}\)
Difference operator
- The difference operator maps
Difference operator
- The difference operator maps
- From values on vertices (0-forms)
Difference operator
- The difference operator maps
- From values on vertices (0-forms)
- To differece values on (half-)edhes (1-forms)
Difference operator
- The difference operator maps
- From values on vertices (0-forms)
- To differece values on (half-)edhes (1-forms)
- Construction for face \(f\) with \(n_f\) vertices/edges \[\mat{d}_f = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & \cdots & 0 & -1\\ -1 & 1 & 0 & \cdots & 0 & 0\\ 0 & -1 & 1 & \cdots & 0 & 0\\ & & & \vdots \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & \dots & -1 & 1\end{pmatrix}\in \R^{n_f \times n_f}\]
- Note that \(\mat{d}\) is rectangular, mapping from all vertices to all halfedges
Properties of DEC Laplacian
\(\laplace \vec{u} \;\approx\; -\mat{M}_0^{-1} \underbrace{\mat{d}\T \mat{M}_1 \mat{d}}_{-\mat{L}} \, \vec{u}\)
- The weak Laplacian \(\mat{L}\) appears as \(-\mat{d}\T \mat{M}_1 \mat{d}\)
- Constants are in kernel of \(\mat{L}\) because \(\mat{d}\) annihilates them 👍
- If \(\mat{M}_1\) is symmetric then \(\mat{L}\) is symmetric 👍
- If \(\mat{M}_1\) is \(regular\) then only the constants are in the kernel 👍
- Linear precision of \(\mat{L}\)?
- Strategy: construction per face as \(\mat{M}_f\)
- Require that \(\mat{L}_f = \mat{d}_f\T \mat{M}_f \mat{d}_f\) yields the area gradient as \(\left(\mat{L}_f\mat{X}_f\right)_i\) for vertex \(i\) 👍
- Problem: linear precision + \(\mat{M}_f\) regular
- Solved by regularization that introduces a parameter that affects the results 👎
Strategy I: The algebraic approach
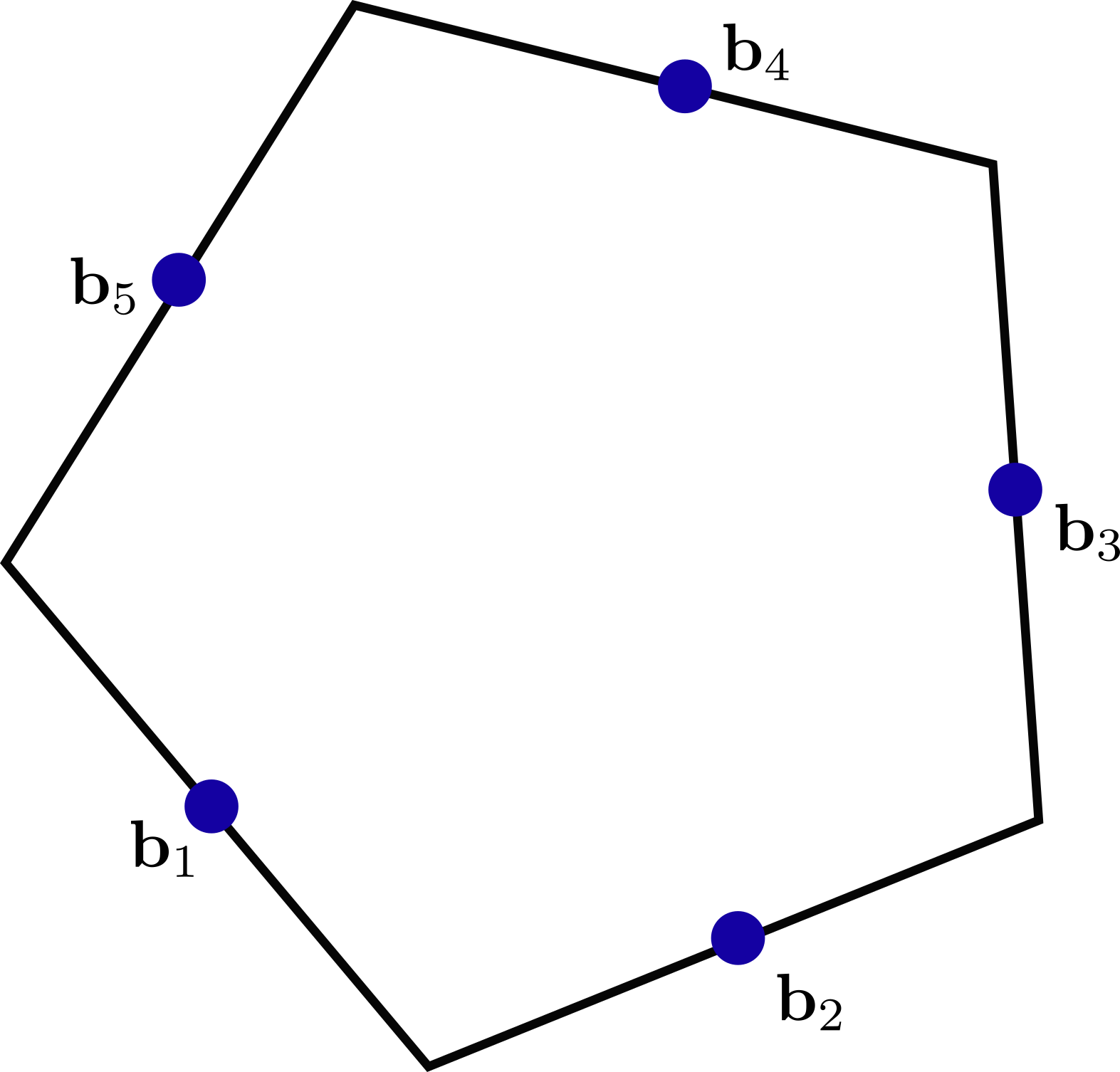
Inner Product Matrix
- \(\mat{B}_f = (\vec{b}_1,\dots,\vec{b}_{n_f})^{\mathsf{T}} \in \R^{n_f \times 3}\)
- Rows are barycenters \(\vec{b}_i = \frac{1}{2}\left(\mat{x}_{i+1}+\vec{x}_i\right)\) of each edge \(\vec{e}_i\).
- $|f| $ is vector area of polygon \(f\)
- Define local inner product matrix for 1-forms \[\mat{\tilde{M}}_f = \frac{1}{|f|}\mat{B}_f \mat{B}_f ^{\mathsf{T}}\]
- Not intuitive / easy to see, but not difficult to prove: \[ \grad_{\vec{x}_i}\abs{f} = \left(\tilde{\mat{L}}_f \mat{X}_f\right)_i \]
- Where \(\tilde{\mat{L}}_f = \mat{d}_f \mat{\tilde{M}}_f \mat{d}\)
Quiz
While \(\mat{\tilde{M}}_f = \frac{1}{|f|}\mat{B}_f \mat{B}_f ^{\mathsf{T}}\) is symmetric PSD by construction it may have a kernel.
Which property is lost for \(-\mat{L}\) when \(\mat{M}_f\) is only semi-definite?
- Symmetry
- Locality
- Linear precision
- Negative semi-definiteness
- Null property
- Positive weights
Fill up the Kernel
- \(\mat{E}_f = (\vec{e}_1,\dots,\vec{e}_{n_f})^{\mathsf{T}} \in \R^{n_f \times 3}\)
- Rows are edge vectors of polygon \(f\).
- Rows are edge vectors of polygon \(f\).
- \(\mathbf{E}_f\T\) has maximal rank 3
- \(\mat{E}_{\bar{f}} = (\bar{\vec{e}}_1,\dots,\bar{\vec{e}}_{n_f})^{\mathsf{T}} \in \R^{n_f \times 3}\)
- Rows are edge vectors of maximal projection \(\bar{f}\).
- Rows are edge vectors of maximal projection \(\bar{f}\).
- \(\mat{E}\T_{\bar{f}}\) has rank 2 \(\rightarrow\) non-trivial kernel
Regularizer
- Add regularizer matrix \(\mat{R}_f\) to fill up kernel \[\mat{M}_{f} = \mat{\tilde{M}}_f + \lambda\mat{R}_f\]
- Built from orthonormal kernel \(\mat{K}_{\bar{f}}\T\) of \(\mat{E}_{\bar{f}}^{\mathsf{T}}\)
- Suggestion: \(\mat{R}_f = \mat{K}_{\bar{f}} \mat{I} \mat{K}_{\bar{f}}\T\)
- Identity \(\mat{I}\) could be replaced with any symmetric PD matrix
Laplace and Mass Matrices
- Local Laplace matrix per polygon \[ {\mat{L}}_f = \mat{d}\T \mat{M}_{f} \mat{d} \]
- Assemble local matrices into global Laplace matrix \(\mat{L}\)
- Global mass matrix \(\mat{M}\) with
\[\mat{M}_{ii} = \sum_{f \ni v_i} \frac{|\bar{f}|}{n_f}\]
Properties
- Symmetry
- Locality
- Linear precision
- Negative semi-definiteness
- Null property
- Positive weights
Poisson System on 2D Voronoi Meshes
13.5053, 28.5194, 58.8386, 119.78, 241.153
Alexa11; λ=2, 0.00838748, 0.00209687, 0.000476346, 0.000127937, 3.30444E-05
Alexa11; λ=1, 0.00456036, 0.0010483, 0.000382806, 8.53325E-05, 1.84683E-05
Alexa11; λ=0.5, 0.00800984, 0.00193734, 0.000621653, 0.000143936, 3.19937E-05
Alexa11; λ=0.1, 0.0144414, 0.00337097, 0.000947331, 0.000221091, 5.14271E-05
<!--
{
"options": {
"scales": {
"x": {
"title": {
"text": "inverse mean edge length",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
},
"y": {
"title": {
"text": "L2 error",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
}
}
}
}
-->Strategy II: Stokes’ Theorem on Cogradient
Quiz
Which part of the integrals causes problems for non-planar polygons? \[\iint_f \grad u(\vec{x}) \d{A} = \oint_{\partial f} u(\vec{x}) \vec{t}(\vec{x}) \times \vec{n}(\vec{x}) \d{\vec{x}} \]
- Tangent vector \(\vec{t}(\vec{x})\) at point \(\vec{x}\)
- Surface normal \(\vec{n}(\vec{x})\) at point \(\vec{x}\)
- The integral over the boundary of the polygon
- The function values \(u(\vec{x})\) at the boundary of the polygon
Cogradient
- Cogradient operator \[\grad u^{\bot}(\vec{x}) := \vec{n}(\vec{x}) \times \grad u(\vec{x}),\]
- Gradient of \(u(\vec{x})\) locally rotated by 90 degrees around normal \(\vec{n}(\vec{x})\)
- Use Stoke’s theorem \[\iint_f \grad u^{\bot}(\vec{x}) \d{A} = \oint_{\partial f} u(\vec{x}) \vec{t}(\vec{x}) \d{\vec{x}}\]
- \(\vec{t}(\vec{x})\) is unit tangent vector at boundary point \(\vec{x}\)
- Well-defined along polygon boundary
Integrated Cogradient
- Consider linear functions \(u\)!
- For linear functions the gradient is constant: \[\iint_f \grad u^{\bot}(\vec{x}) \d{A} = \iint_f \vec{n}(\vec{x}) \times \grad u(\vec{x}) \d{A} = \left(\iint_f \vec{n}(\vec{x}) \d{A}\right) \times \grad u(\vec{x})\]
- Integrated normal \(\vec{n}(\vec{x})\) is the area vector \(\vec{a}_f\)
- Independent of spanning surface
- Can be computed from boundary (polygon)
- The contour integral becomes a sum over edge vectors times average values on edges: \[\oint_{\partial f} u(\vec{x}) \vec{t}(\vec{x}) \d{\vec{x}} = \mat{E}_f\T\mat{A}_f\]
- Gives expression for polygon gradient operator \(\vec{G}_f = -\|\vec{a}_f\|^{-2}\vec{a}_f \times \mat{E}_f\T\mat{A}_f\)
Musical Operators
- Construction of Laplace operator from gradient leads to non-trivial kernel
- Similar to previous construction
- More careful construction using musical operators
- Flat \((\flat)\) operator transforms vector to 1-form
- Sharp \((\sharp)\) operator transforms 1-form to vector
- Sharp operator defines gradient in smooth setting \(\grad u = (\d u)^{\sharp}\)
- Discrete version: \(\mat{G}_f = \mat{V}_f^{\sharp}\mat{d}_f\)
- \(\mat{V}_f^{\sharp}\) maps
- From 1-form (difference values at edges)
- To vector in the polygon plane (tangent vector)
- Use \(\mat{G}_f\) to construct \(\mat{V}_f^{\sharp}\)
- \(\mat{V}_f^{\sharp}\) maps
First Attempt for Inner Product Matrix
\[\mat{\tilde{M}}_f = \abs{\bar{f}} \, \mat{V}_f^{\sharp \mathsf{T}} \, \mat{V}_f^{\sharp}\]
- \(\mat{\tilde{M}}_f\) is a dot product of tangent vectors
- Mapping \(n_f\) values to tangent vector leads to loss of information 😢
- Add regularizer for kernel dimension 👍
Regularizer
- Add regularizer matrix \(\mat{R}_f\) to fill up kernel \[\mat{M}_{f} = \mat{\tilde{M}}_f + \lambda\mat{R}_f\]
- Construct flat operator \(\mat{V}_f^{\flat}\)
- Use that \(\mat{V}_f^{\sharp}\mat{V}_f^{\flat}\) preserves tangent vectors
- Projection \(\mat{P}_f = \mat{I} - \mat{V}_f^{\flat}\mat{V}_f^{\sharp}\) encodes loss from projecting to tangent vectors
- Regularizer \(\mat{R}_f = \mat{P}_f\T\mat{P}_f\) spans the non-trivial kernel
- Construct flat operator \(\mat{V}_f^{\flat}\)
Laplace and Mass Matrices
- Local Laplace matrix per polygon \[ {\mat{L}}_f = \mat{d}\T \mat{M}_f\mat{d} \]
- Assemble into global matrix \(\mat{L}\)
- Global mass matrix \(\mat{M}\) same as Alexa and Wardetzky
Properties
- Symmetry
- Locality
- Linear precision
- Negative semi-definiteness
- Null property
- Positive weights
Poisson System on 2D Voronoi Meshes
13.5053, 28.5194, 58.8386, 119.78, 241.153
deGoes20; λ=2, 0.00965471, 0.00245388, 0.000542276, 0.000145297, 3.74297E-05
deGoes20; λ=1, 0.00435302, 0.000996788, 0.000354402, 7.95537E-05, 1.73643E-05
deGoes20; λ=0.5, 0.00747841, 0.00182759, 0.00059557, 0.000138136, 3.05869E-05
deGoes20; λ=0.1, 0.0139834, 0.00327528, 0.00092799, 0.000217473, 5.03785E-05
<!--
{
"options": {
"scales": {
"x": {
"title": {
"text": "inverse mean edge length",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
},
"y": {
"title": {
"text": "L2 error",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
}
}
}
}
-->Demo: Curvature
Outline
- Introduction
- Laplacian for Triangle Meshes
- Laplacian for Polygon Meshes
- Martin et al., Polyhedral finite elements using harmonic basis functions, SGP 2008
- Alexa & Wardetzky, Discrete Laplacians on general polygonal meshes, SIG 2011
- de Goes et al., Discrete differential operators on polygonal meshes, SIG 2020
- Bunge et al., Polygon Laplacian made simple, EG 2020
- Bunge et al., The Diamond Laplace for polygonal and polyhedral meshes, SGP 2021
- Bunge et al., Variational quadratic shape functions for polygons and polyhedra, SIG 2022
- Comparisons & Conclusion
Virtual Simplicial Refinement
Prolongation Operator
\[ {\Huge \downarrow} \; \mat{P} \]
- Insert virtual vertex as affine combination \[ \small \matrix{ \sum_i w_i \vec{x}_{i}\\ \vec{x}_{1}\\ \vec{x}_{2}\\ \vec{x}_{3}\\ \vec{x}_{4}\\ \vec{x}_{5}\\ \vec{x}_{6} } = \underbrace{ \matrix{ w_1 & w_2 & w_3 & w_4 & w_5 & w_6\\ 1 & & & & & \\ & 1 & & & & \\ & & 1 & & & \\ & & & 1 & & \\ & & & & 1 & \\ & & & & & 1 } }_{\mat{P}} \matrix{ \vec{x}_{1}\\ \vec{x}_{2}\\ \vec{x}_{3}\\ \vec{x}_{4}\\ \vec{x}_{5}\\ \vec{x}_{6} } \]
Restriction Operator
\[ {\Huge \uparrow} \; \mat{R} = \mat{P}\T \]
- Redistribute values back to original nodes \[ \mat{R} = \mat{P}\T \]
Polygon Shape Functions
\[\downarrow\]
\[\downarrow\]
- Insert center vertex through prolongation weights
- Compute standard linear shape functions \(\psi_j(\vec{x})\) on refined polygon
- Coarse shape function for polygon \((\vec{x}_1, \dots, \vec{x}_n)\) with virtual vertex \(\vec{x}_0\) become \[ \varphi_i(\vec{x}) = \psi_i(\vec{x}) + w_i\psi_0(\vec{x}) \,,\quad i \in \{1, \dots, n\} \]
Polygon Shape Functions
- Piecewise linear functions
- Interpolate nodal data: \(\varphi_i\of{\vec{x}_j} = \delta_{ij}\)
- Partition of unity: \(\sum_i \varphi_i\of{\vec{x}} = 1\)
- Barycentric property: \(\sum_i \varphi_i\of{\vec{x}} \vec{x}_i = \vec{x}\)
- \(C^0\) across elements, not \(C^1\) within elements
Choice of Virtual Vertex
Solve linear system for affine prolongation weights 👍
Quiz
For which (planar) elements would the virtual vertex lead to flipped virtual triangles?
- Star-shaped elements
- Convex elements
- Non-star-shaped elements
- Concave elements
Laplace Matrix & Mass Matrix
- “Sandwiched” Laplace matrix for polygons \[\mat{L} = \mat{P}\T \, \mat{L}^\func{tri} \, \mat{P} \]
- “Sandwiched” mass matrix for polygons \[\mat{M} = \mat{P}\T \, \mat{M}^\func{tri} \, \mat{P} \]
- Laplacian can be factored into divergence and gradient \[ \mat{L} = \underbrace{\mat{P}\T \mat{D}^\func{tri}}_{\mat{D}} \cdot \underbrace{\mat{G}^\func{tri} \mat{P}}_{\mat{G}} \]
Virtual refinement is completely hidden in matrix assembly step!
Demo: Smoothing
Properties
- Symmetry
- Locality
- Linear precision
- Negative semi-definiteness
- Null property
- Positive weights
Poisson System on 2D Voronoi Meshes
13.5053, 28.5194, 58.8386, 119.78, 241.153
Bunge20, 0.00768401,0.00193955,0.00057802,0.000152567,3.41754E-05
<!--
{
"options": {
"scales": {
"x": {
"title": {
"text": "inverse mean edge length",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
},
"y": {
"title": {
"text": "L2 error",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
}
}
}
}
-->Linear Shape Functions for Polyhedra
- Insert virtual face point
- Minimizer of squared triangle areas
- Insert virtual cell point
- Minimizer of squared tetrahedra volumes
- Two-step prolongation \[ \mathbf{P} = \mat{P}_c \, \mat{P}_f\]
Outline
- Introduction
- Laplacian for Triangle Meshes
- Laplacian for Polygon Meshes
- Martin et al., Polyhedral finite elements using harmonic basis functions, SGP 2008
- Alexa & Wardetzky, Discrete Laplacians on general polygonal meshes, SIG 2011
- de Goes et al., Discrete differential operators on polygonal meshes, SIG 2020
- Bunge et al., Polygon Laplacian made simple, EG 2020
- Bunge et al., The Diamond Laplace for polygonal and polyhedral meshes, SGP 2021
- Bunge et al., Variational quadratic shape functions for polygons and polyhedra, SIG 2022
- Comparisons & Conclusion
Finite Volumes
Main idea: Consider the integral of differential in a small region
- Divergence: \[\iint_{\Omega} \text{div} \vec{u}\ \d{A} = \oint_{\partial \Omega} \vec{u}\tp\vec{n} \d{s}\]
- Gradient: \[\iint_\Omega \nabla u \d{A} = \oint_{\partial \Omega} u\, \mat{n} \d{s}\]
- Laplacian: \[\iint_\Omega \Delta u \d{A} = \oint_{\partial \Omega} \nabla u\tp \mat{n} \d{s}\]
Discrete Duality Finite Volumes (DDFV)
Quiz
How do we get diamond cells on an arbitrary polygon mesh?
- Subdivide into triangles
- Subdivide into quads
- Connect primal and dual vertices
- Introduce third control mesh
2D DDFV
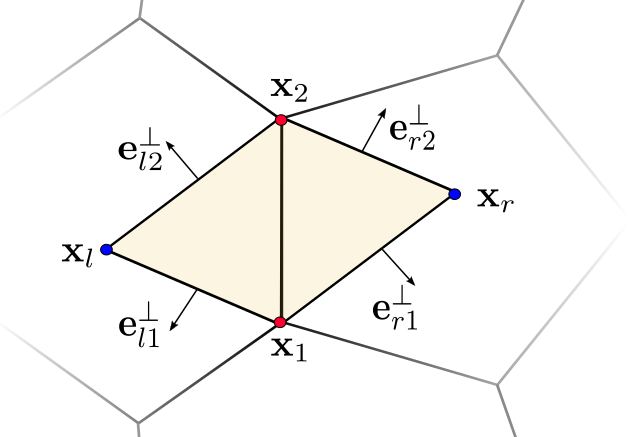
\[ \grad u|_D \;=\; \frac{1}{2 \abs{D}} \sum_{(i,j) \in \partial D} \vec{e}_{ij}^\perp \frac{u_i+u_j}{2} \]
Limitations of DDFV
- Typically only primal mesh is given
- Dual vertices increase DoF significantly
- Only defined on 2D planar meshes, not on two-manifolds
Virtual Dual Vertices
\[\downarrow\]
\[\downarrow\]
- Combine ideas from DDFV and virtual refinement
- Use virtual vertices as dual mesh
- Compute DDFV operator on the “virtual diamonds”
- Express diamond in an intrinsic 2D coordinate system
- Restrict values back to the original mesh
Limitations of DDFV
- Typically only primal mesh is given
- Dual vertices increase DoF significantly
- Only defined on 2D planar meshes, not on two-manifolds
Diamond Gradient Operator
- The \(i\)-th column of the diamonds gradient matrix \(\mat{G}_D \in \R^{2 \times 4}\) \[ \mat{G}_D(:,i) = \frac{1}{2 \abs{D}} \sum_{(i,j) \in \partial D} \vec{e}_{ij}^\perp \]
- Mesh gradient \(\hat{\mat{G}}\) is combined with prolongation \(\mat{P}\) to form global operator \[ \mat{G} = \hat{\mat{G}} \, \mat{P} \,\in\R^{2\abs{\mathcal{E}} \times \abs{\mathcal{V}}} \]
Diamond Divergence Operator
- The diamond divergence matrix is defined as \[ \mat{D} = -\mat{P}\tp \hat{\mat{G}}\tp \hat{\mat{M}}_\diamond \]
- \(\hat{\mat{M}}_\diamond\) is diagonal matrix of diamond areas
Laplace Operator
- Laplacian matrix is defined as \[ \mat{L} \;=\; \underbrace{-\mat{P}\tp \hat{\mat{G}}\tp \hat{\mat{M}}_\diamond}_{\mat{D}} \cdot \underbrace{\hat{\mat{G}} \mat{P}}_{\mat{G}} \]
- Mass matrix derived from standard DDFV mass matrix \(\mat{M}_\diamond\) \[ \mat{M} \;=\; \mat{P}\tp \mat{M}_\diamond \mat{P} \]
Demo: Geodesics
Properties
- Symmetry
- Locality
- Linear precision
- Negative semi-definiteness
- Null property
- Positive weights
Poisson System on 2D Voronoi Meshes
13.5053, 28.5194, 58.8386, 119.78, 241.153
Diamond, 0.00610683,0.00155889,0.000413685,0.000105977,2.46064E-05
<!--
{
"options": {
"scales": {
"x": {
"title": {
"text": "inverse mean edge length",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
},
"y": {
"title": {
"text": "L2 error",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
}
}
}
}
-->Diamond Laplace on Polyhedral Meshes
- Same two-step prolongation as linear virtual refinement method \[ \mathbf{P} = \mat{P}_c \, \mat{P}_f\]
- Construct minimal diamond cells
Volume Diamond Gradient
Outline
- Introduction
- Laplacian for Triangle Meshes
- Laplacian for Polygon Meshes
- Martin et al., Polyhedral finite elements using harmonic basis functions, SGP 2008
- Alexa & Wardetzky, Discrete Laplacians on general polygonal meshes, SIG 2011
- de Goes et al., Discrete differential operators on polygonal meshes, SIG 2020
- Bunge et al., Polygon Laplacian made simple, EG 2020
- Bunge et al., The Diamond Laplace for polygonal and polyhedral meshes, SGP 2021
- Bunge et al., Variational quadratic shape functions for polygons and polyhedra, SIG 2022
- Comparisons & Conclusion
Linear Elasticity
Locking due to high Poisson ratio 😢
Linear vs Quadratic
Quiz
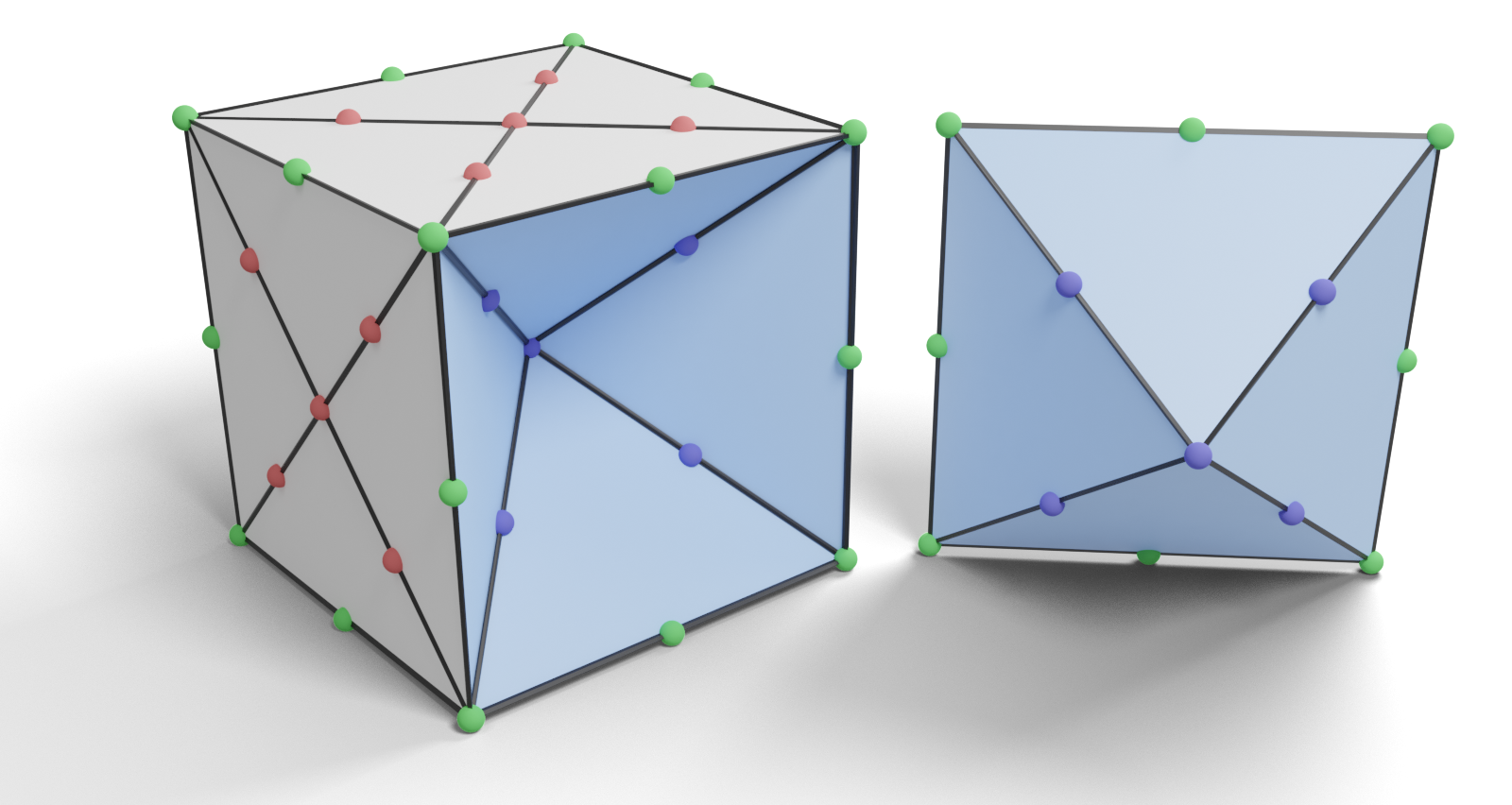
Given a quad, how many virtual degrees of freedom do we need for the quadratic Lagrange elements?
- Four virtual vertices
- Five virtual vertices
- Twelve virtual vertices
- Thirteen virtual vertices
Quiz
Given a quad, how many virtual degrees of freedom do we need for the quadratic Lagrange elements?
Quadratic Polygon Shape Functions
- Compute standard quadratic shape functions \(\psi_j(\vec{x})\) on refined polygon
- Shape functions for polygon \((\vec{x}_1, \dots, \vec{x}_n)\) with coarse DoFs \(\mathcal{C}\) and virtual DoFs \(\mathcal{K}\) \[ {\color{green}\varphi_i(\vec{x})} = {\color{green}\psi_i(\vec{x})} + \sum_{j\in \mathcal K} w_{ij} {\color{red} \psi_j(\vec{x})} \quad\text{ for } i \in \mathcal C. \]
Prolongation Weights Influence Convergence
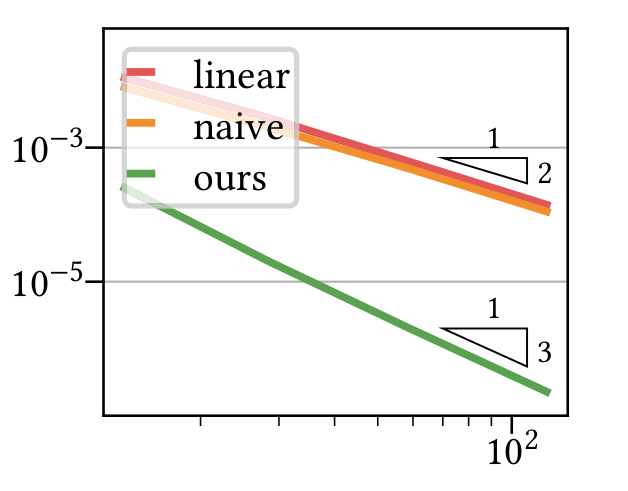
Optimize for Smoothness
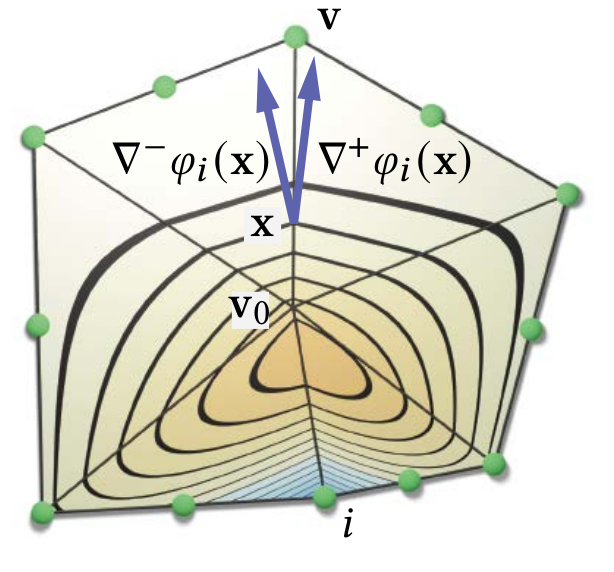
- Shape functions for polygon \((\vec{x}_1, \dots, \vec{x}_n)\) \[ {\color{green}\varphi_i(\vec{x})} = {\color{green}\psi_i(\vec{x})} + \sum_{j\in \mathcal K} w_{ij} {\color{red} \psi_j(\vec{x})} \quad\text{ for } i \in \mathcal C. \]
- Solve variational optimization per cell \[ \min_{\{w_{ij}\}} \sum_{i \in \mathcal C} \sum_{\sigma \in \mathcal E^*} \int_\sigma \norm{ \nabla_\sigma^+ \varphi_i - \nabla_\sigma^- \varphi_i }^2 \ \mathrm{d}\sigma \]
- Only needs a linear system solve 👍
Properties of Shape Functions
- Reproduce \(P2\) on triangle meshes (proven)
- Lagrange interpolation property (by construction)
- Partition of unity (hard constraint)
- Linear precision (hard constraint)
- Quadratic precision (empirical observation)
Linear Elasticity

Geodesic Distances
Poisson System on 2D Voronoi Meshes
13.5053, 28.5194, 58.8386, 119.78, 241.153
Quadratic Virtual Refinement, 0.000249856,1.9939E-05,2.01787E-06,2.2815E-07,2.72628E-08
<!--
{
"options": {
"scales": {
"x": {
"title": {
"text": "inverse mean edge length",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
},
"y": {
"title": {
"text": "L2 error",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
}
}
}
}
-->Poisson System on 2D Voronoi Meshes
13.5053, 28.5194, 58.8386, 119.78, 241.153
Harmonic, 0.00951959, 0.00236579, 0.000699382, 0.000188646, 5.46139E-05
Alexa11; λ=2, 0.00838748, 0.00209687, 0.000476346, 0.000127937, 3.30444E-05
Alexa11; λ=1, 0.00456036, 0.0010483, 0.000382806, 8.53325E-05, 1.84683E-05
Alexa11; λ=0.5, 0.00800984, 0.00193734, 0.000621653, 0.000143936, 3.19937E-05
Alexa11; λ=0.1, 0.0144414, 0.00337097, 0.000947331, 0.000221091, 5.14271E-05
deGoes20; λ=2, 0.00965471, 0.00245388, 0.000542276, 0.000145297, 3.74297E-05
deGoes20; λ=1, 0.00435302, 0.000996788, 0.000354402, 7.95537E-05, 1.73643E-05
deGoes20; λ=0.5,0.00747841, 0.00182759, 0.00059557, 0.000138136, 3.05869E-05
deGoes20; λ=0.1,0.0139834, 0.00327528, 0.00092799, 0.000217473, 5.03785E-05
Linear Virtual Refinement, 0.00768401, 0.00193955, 0.00057802, 0.000152567, 3.41754E-05
Diamond, 0.00610683,0.00155889,0.000413685,0.000105977,2.46064E-05
Quadratic Virtual Refinement, 0.000249856,1.9939E-05,2.01787E-06,2.2815E-07,2.72628E-08
<!--
{
"options": {
"scales": {
"x": {
"title": {
"text": "inverse mean edge length",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
},
"y": {
"title": {
"text": "L2 error",
"display": true
},
"type": "logarithmic"
}
}
}
}
-->Quadratic Shape Functions for Polyhedra
\[ \small \min_{\{w_{ij}\}} \sum_{i \in \mathcal C} \sum_{\sigma \in \mathcal T^*} \int_\sigma \norm{\nabla_\sigma^+ \varphi_i - \nabla_\sigma^- \varphi_i}^2 \mathrm{d}\sigma \]
Quadratic Shape Functions for Polyhedra

Linear Elasticity
Outline
- Introduction
- Laplacian for Triangle Meshes
- Laplacian for Polygon Meshes
- Martin et al., Polyhedral finite elements using harmonic basis functions, SGP 2008
- Alexa & Wardetzky, Discrete Laplacians on general polygonal meshes, SIG 2011
- de Goes et al., Discrete differential operators on polygonal meshes, SIG 2020
- Bunge et al., Polygon Laplacian made simple, EG 2020
- Bunge et al., The Diamond Laplace for polygonal and polyhedral meshes, SGP 2021
- Bunge et al., Variational quadratic shape functions for polygons and polyhedra, SIG 2022
- Comparisons & Conclusion
Quantitative Comparisons
- Ensure fair comparisons
- All methods (re)implemented in C++
- Same meshes & test for all methods
- Code checked by original authors (Thanks 👍)
- Source code for all Laplace operators, quantitative tests, and interactive demos is available on github
Poisson System on 2D Planes
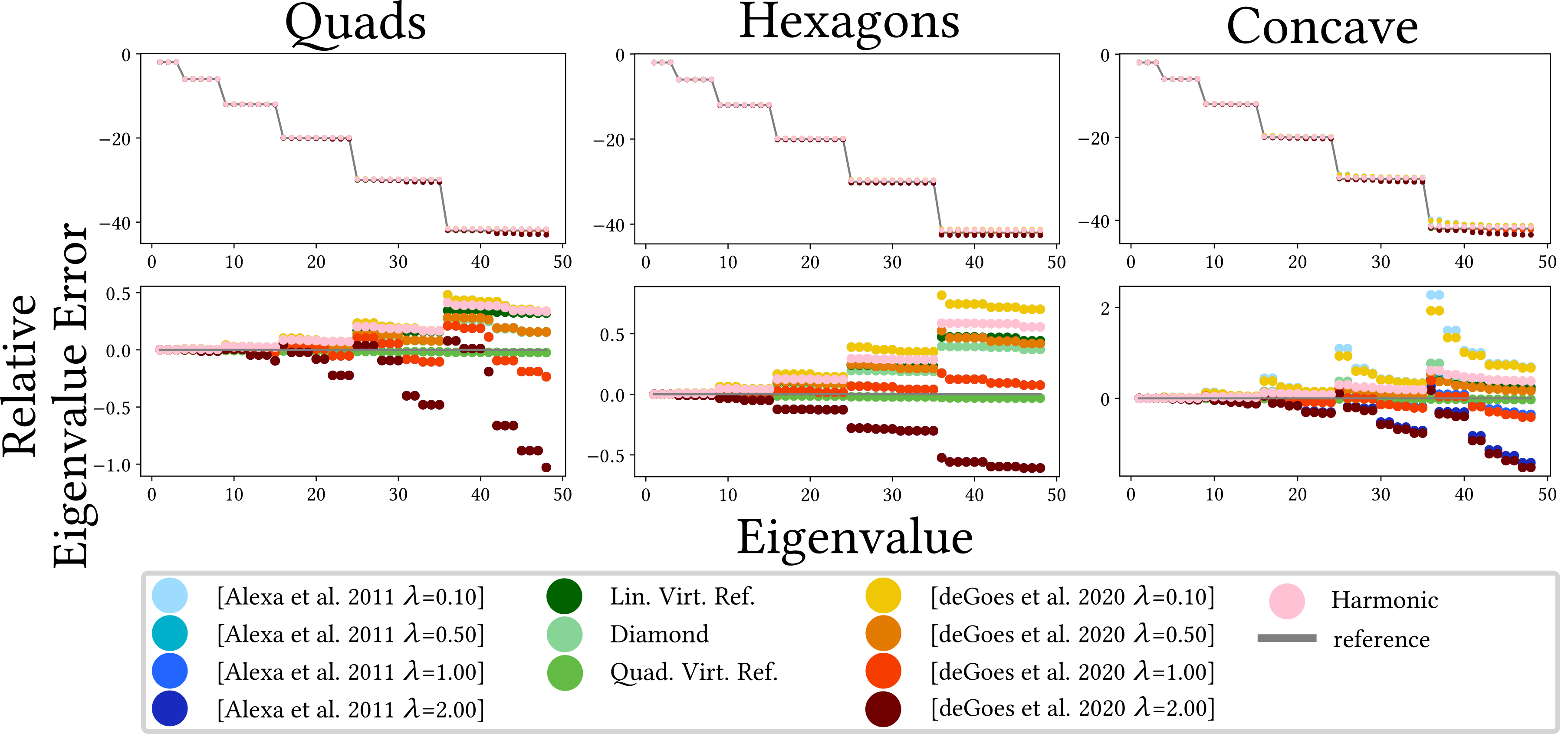
Eigenvalues on Unit Spheres
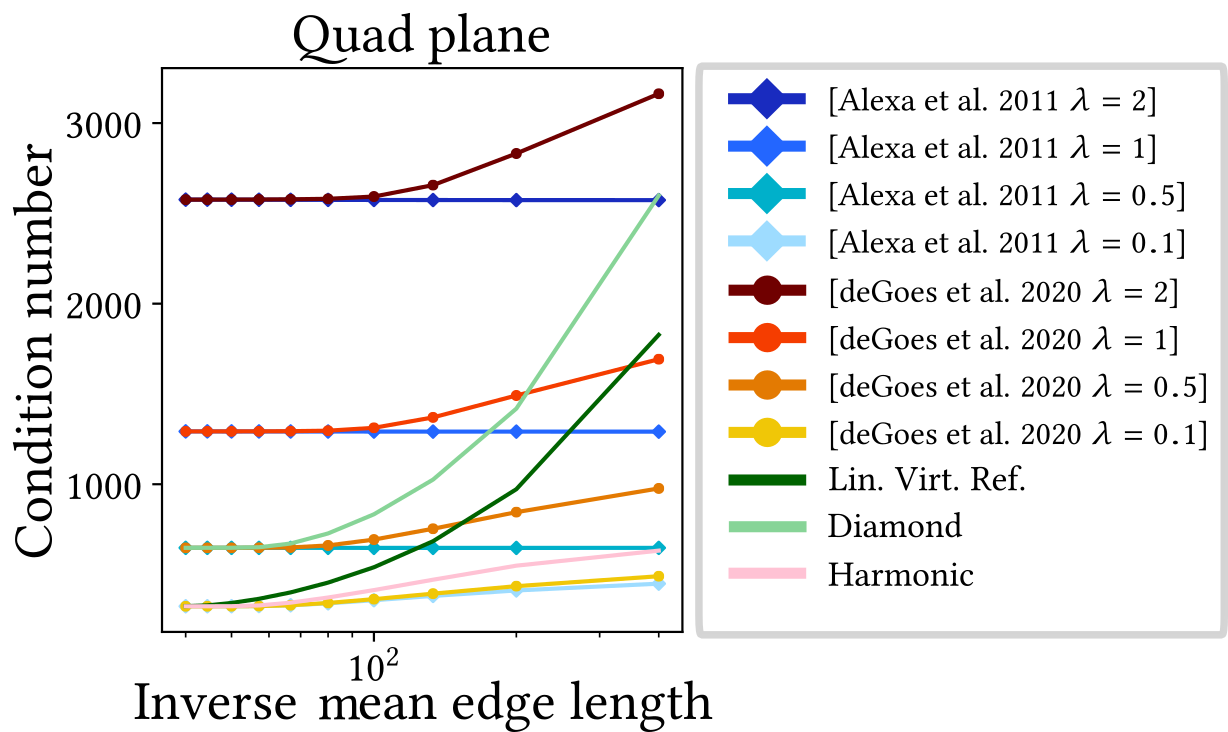
Condition Number
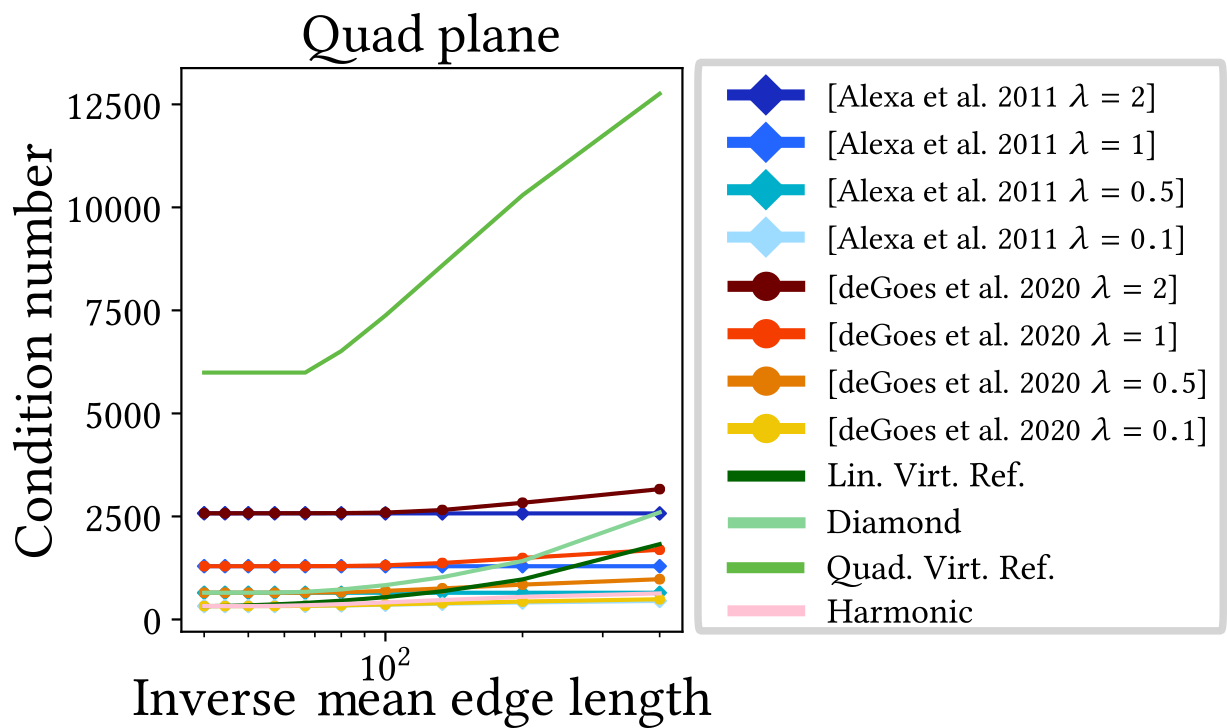
Condition Number
Computational Performance
Computational Performance
Conclusion
Recommendations
- DEC Approaches
- Favorable numerical results
- Many other operators (de Goes et al.)
- Stabilization term has to be adjusted
- Diamond Laplacian
- Works on surfaces and volumes
- Favorable numerical results
- Longer solving times
- Virtual Refinement Method
- Works on surfaces and volumes
- Linear version slightly less accurate
- Easy to implement (linear)
- Quadratic version very accurate
- Not as easy to implement (quadratic)
- Longer solving times (quadratic)
- Harmonic shape functions
- Work on surfaces and volumes
- Generalize \(P1\) and \(Q1\) elements
- Computationally expensive
💾 Source code of all methods available on github 💾
Conclusion
- Presented recent progress for Polygon Laplacians
- Discuss individual discretization strategies
- Point out similarities and differences
- Analyze individual strength and weaknesses
- Extensions
- More details on volume meshes (see course notes)
- Acknowledgments
- Collaborators: Philipp Herholz, Misha Kazhdan, Olga Sorkine-Hornung
- Code-Checkers: Fernando de Goes, Max Wardetzky
References